
Over 300 dancers and musicians will perform, who will also teach visitors the traditional 'Csárdás' dance.Continue reading
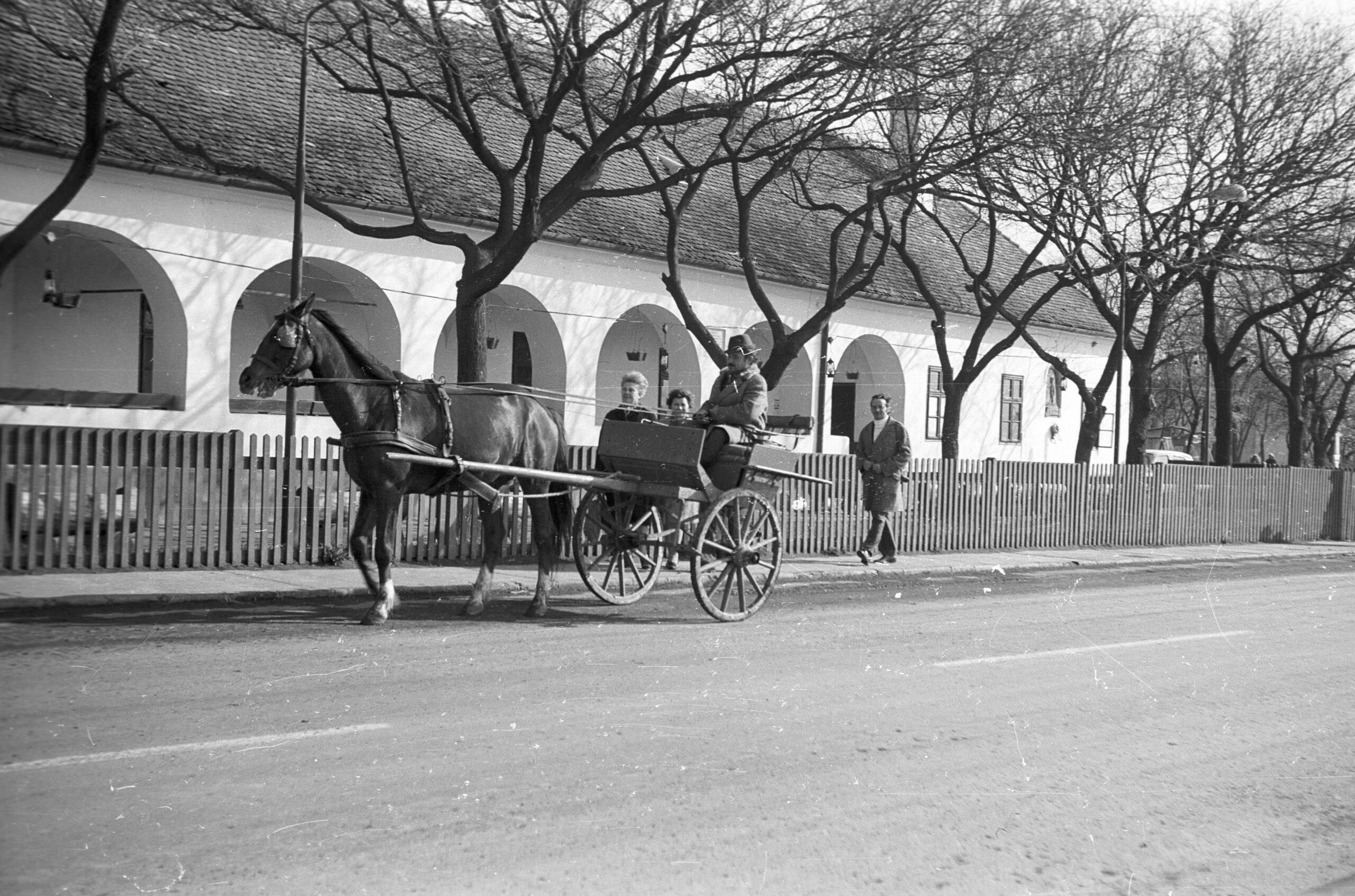

The Committee for Hungarikums declared the csárda (traditional Hungarian inn) and Badacsony kéknyelű (Hungarian grape variety grown exclusively in the Badacsony region, Lake Balaton) to be Hungarikums, meaning they are now recognized as official Hungarian cultural treasures. The Conductive Education System based on the Pető method, as well as Békés County furriers’ embroidery and the Hungarian saddle, were added to the Hungarian Heritage Collection. This brings the number of items in the Collection of Hungarikums to 96 and the Hungarian Heritage Collection to 158, according to a statement issued by the Ministry of Agriculture on Thursday.
The Ministry explained that the Collection of Hungarikums now includes the csárda, a traditional Hungarian hospitality establishment that has been operating as a place of lodging and catering since the early modern period and continues to exist today.
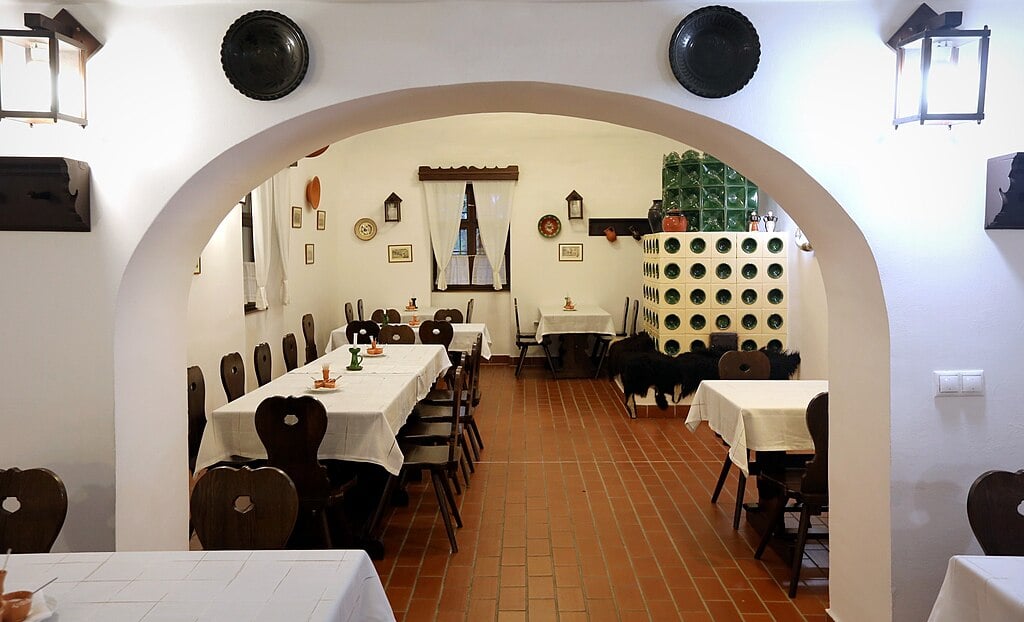

Interior of the Hortobágy Csárda nowadays. Photo: Wikimedia Commons
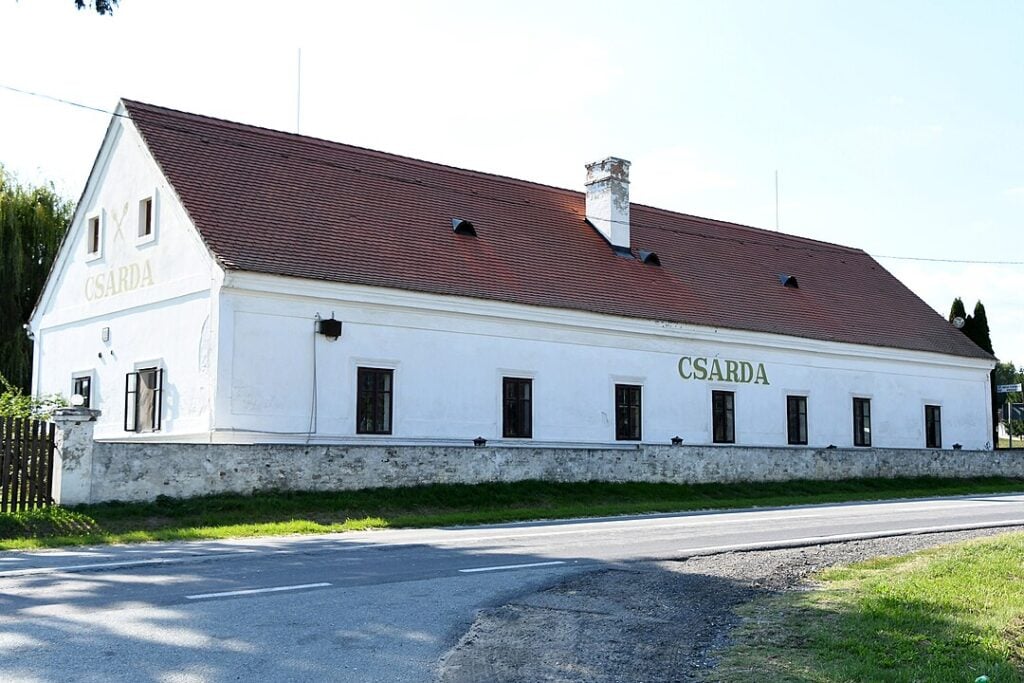

Csárda in Magyarszerdahely (western Hungary). Photo: Wikimedia Commons
In a video message posted on his social media page following the meeting of the Committee in Hortobágy, Minister of Agriculture István Nagy said that
the over 300-year-old Hortobágy Csárda, which hosted the committee meeting, is an integral part of Hungarian culture, preserving and conveying values, and we should be infinitely proud of this.”
The Badacsony kéknyelű grape variety has also been declared a Hungarikum. “This is particularly important to us because this grape variety is grown on just 45 hectares. There have even been occasions when wine made from this grape has been voted the best in the world.
Kéknyelű is considered by experts to be an autochthonous variety, i.e. an ancient variety that has remained in its place of origin, and is therefore considered a native variety,”
Minister Nagy explained.
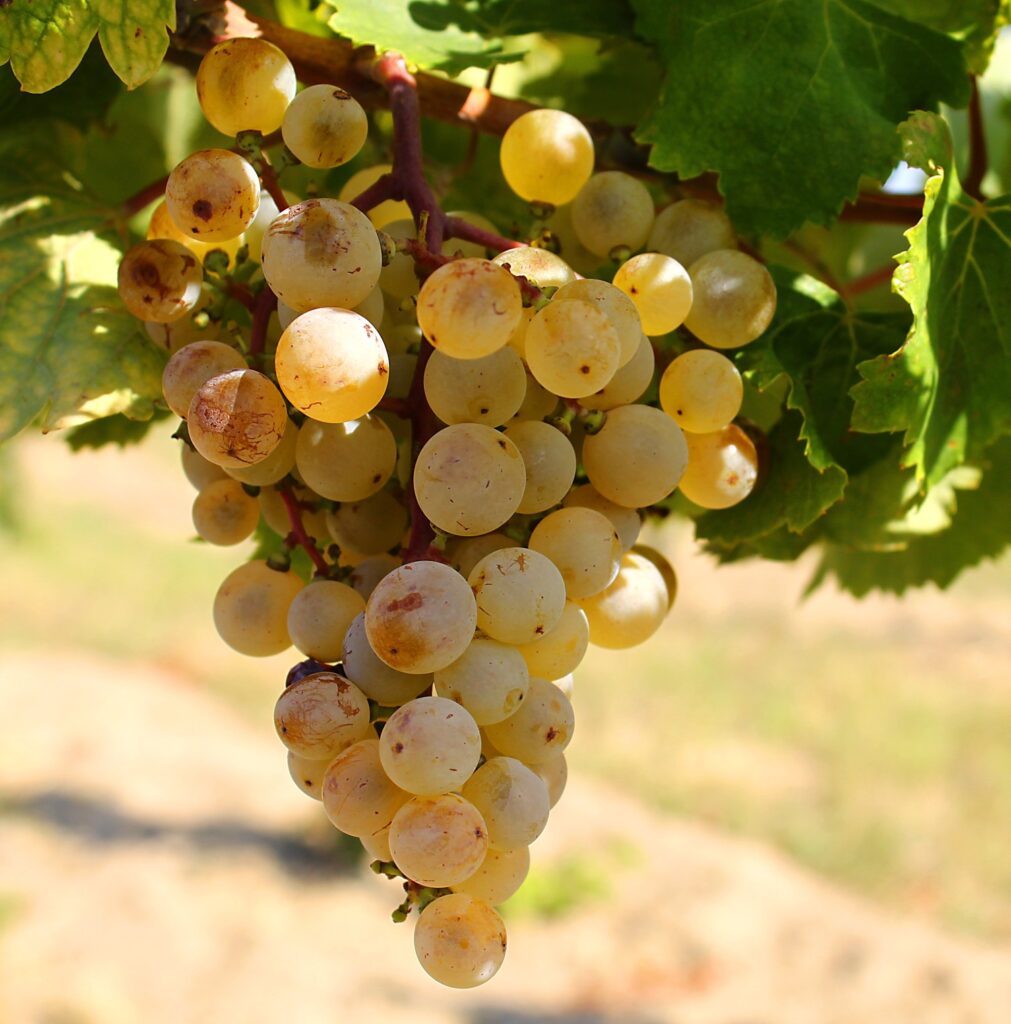

Keknyelű grape cluster. Photo: Wikipedia
The Conductive Education System, based on the Pető method, has been included in the Hungarian Heritage Register. It helps people with physical disabilities in their physical and mental development, in regaining their abilities, and in better integration into society.
It is unique in the world that conductive education is part of both public education and public health in Hungary.
From today, the Békés County furriers’ embroidery (furriery) is also part of the Hungarian Heritage Collection. The Minister of Agriculture said that this craft is still practiced by living communities today, and that it is important to recognize it in order to pass on these traditions to future generations. The furriers’ embroidery in Békés County appeared in an organized form in the first half of the 18th century, when the first guild was established. In the 19th century, the economic development of the county led to an increased demand for high-quality home furnishings and more fashionable clothing. Ornately embroidered coats and jackets were common items of clothing for the population of Békés County.
In 2021, the “living tradition of furriers’ embroidery in Békés County” was added to the National Register of Intangible Cultural Heritage.
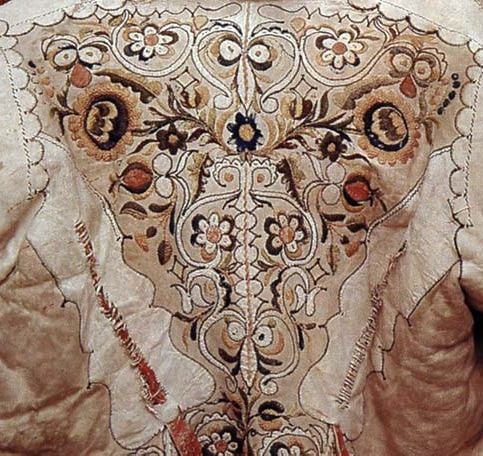
Photo: Wikipedia
The Minister emphasized that the committee is very proud that the Hungarian saddle, “which played a key role in many heroic deeds,” has also been added to the register. The committee’s report reveals that “based on research to date and studies of the richest and most prestigious public collections, we can conclude that our saddle is part of our Eastern cultural heritage, which underwent a certain internal development process after the settlement of the Carpathian Basin. The result of this is the Hungarian saddle, and its most widespread variant, the Tiszafüred saddle, which was held in high esteem in the everyday life and festive occasions of our peasantry until it was forced out of use.”
Via MTI, Featured image: Fortepan / Zoltán Lencse